Aortic Aneurysm
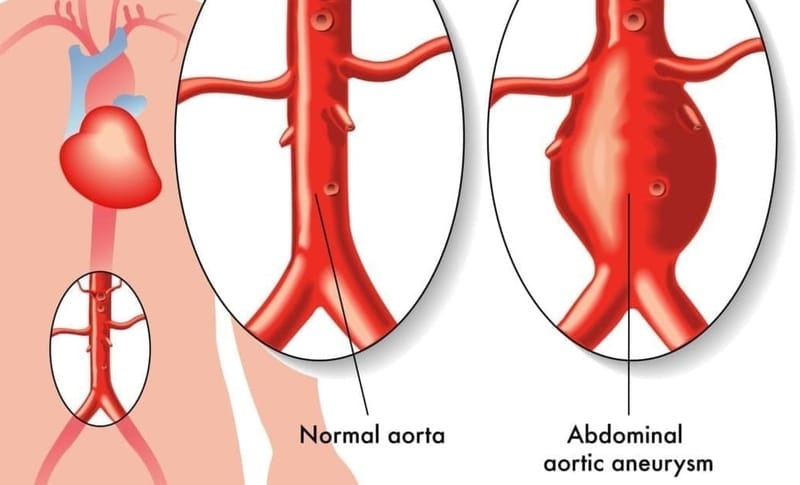
An aortic aneurysm is a balloon-like bulge in the aorta, the large artery that carries blood from the heart through the chest and torso.
Aortic aneurysms can dissect or rupture:
The force of blood pumping can split the layers of the artery wall, allowing blood to leak in between them. This process is called a dissection.
The aneurysm can burst completely, causing bleeding inside the body. This is called a rupture.
Dissections and ruptures are the cause of most deaths from aortic aneurysms.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair?
Your doctor may recommend abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair to treat an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a bulging, weak spot in the aorta that may be at risk for rupturing. In this case, the aneurysm is in part of the aorta that is in the abdomen. Repair of an AAA may be done in one of two ways:
Open repair. For this surgery, your doctor makes a large incision in the abdomen to expose the aorta. Once he or she has opened the abdomen, a graft can be used to repair the aneurysm. Open repair remains the standard procedure for an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). This is a minimally invasive option. This means it is done without a large incision. Instead, the doctor makes a small incision in the groin. He or she will insert special instruments through a catheter in an artery in the groin and thread them up to the aneurysm. At the aneurysm, your doctor will place the stent and graft to support the aneurysm.
What are the risks of AAA repair?
As with any surgical procedure, complications can occur. Some possible complications may include:
Open repair
Heart attack
Irregular heart rhythms
Bleeding during or after surgery
Injury to the bowel
Loss of blood flow to legs or feet from a blood clot
Blood clot
Infection of the graft
Lung problems
Kidney damage
Spinal cord injury
EVAR
Damage to surrounding blood vessels, organs, or other structures
Kidney damage
Loss of blood flow to leg or feet from a blood clot
Groin wound infection
Groin hematoma (large blood-filled bruise)
Bleeding
Endoleak (continual leaking of blood out of the graft and into the aneurysm sac with potential rupture)
Spinal cord injury


