Carotid Artery Stenosis
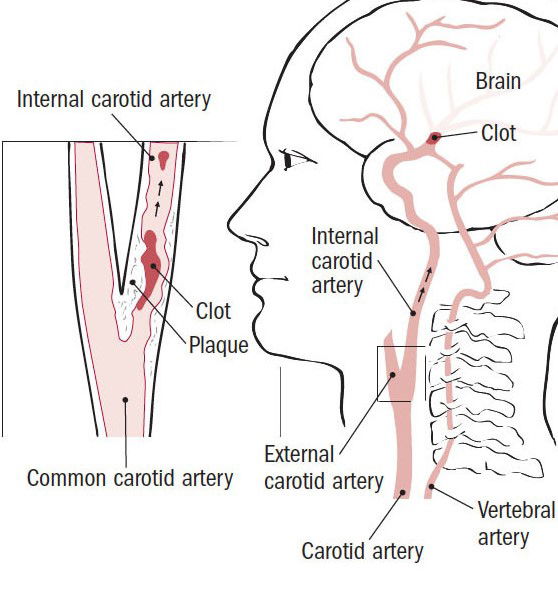
Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing of the large arteries on either side of the neck. These arteries carry blood to the head, face, and brain. This narrowing is usually the result of a build-up of plaque within the arteries, a condition called atherosclerosis. Stenosis can worsen over time to completely block the artery which may lead to stroke.
What is a carotid endarterectomy?
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is surgery to treat carotid artery disease. The carotid arteries are the main blood vessels that carry oxygen and blood to the brain. In carotid artery disease, these arteries become narrowed. This reduces blood flow to the brain and could cause a stroke.
During a carotid endarterectomy, your surgeon will surgically remove plaque that builds up inside the carotid artery. He will make a cut (incision) on the side of the neck over the affected carotid artery. The artery is opened and the plaque removed. Your surgeon will stitch the artery back together. This restores normal blood flow to the brain.
Why might I need a carotid endarterectomy?
Narrowing of the carotid arteries is most often caused by atherosclerosis. This is a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of the artery. Plaque is made up of fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste products, calcium, and fibrin. Atherosclerosis is also called "hardening of the arteries." It can affect arteries throughout the body. Carotid artery disease is similar to coronary artery disease. In coronary artery disease, blockages form in the arteries of the heart and may cause a heart attack. In the brain, it can lead to stroke.
The brain needs a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to work correctly. Even a brief break in blood supply can cause problems. Brain cells start to die after just a few minutes without blood or oxygen. If the narrowing of the carotid arteries becomes severe enough to block blood flow, or a piece of plaque breaks off and blocks blood flow to the brain, a stroke may happen. A mini-stroke (transient ischemic attack or TIA) is stroke like-symptoms that last only a few minutes to a few hours. A TIA may be the first sign of the disease.
You may not have symptoms if you have carotid artery disease. Plaque buildup may not be blocking enough blood flow to cause symptoms. An artery that is blocked only halfway or less often does not cause any symptoms.
What are the risks of a carotid endarterectomy?
Some possible complications of carotid endarterectomy include:
- Stroke or TIA
- Heart attack
- Pooling of blood into tissue around the incision site causing swelling
- Nerve problems with certain functions of the eyes, nose, tongue, or ears
- Bleeding into the brain (intracerebral hemorrhage)
- Seizures (uncommon)
- Repeated blockage of the carotid artery. Or new blockage that develops in the artery on the other side of your neck.
- Bleeding at the incision site in the neck
- Infection
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heart beat
- Blocked airway from swelling or from bleeding in the neck
There may be other risks based on your condition. Discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before the procedure.


